Click to zoom
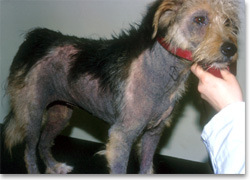
Extensive hyperpigmentation in a dog with chronic Malassezia
dermatitis |
|
Skin pigmentation depends primarily on the nature and amount
of melanin within epidermal cells.
Pigmentation is often increased in endocrine diseases affecting
the skin or as a consequence of inflammation. Inflammatory
processes may conversely lead to hypopigmentation if melanocytes
are damaged (eg in autoimmune diseases centred on the dermo-epidermal
junction such as lupus erythematosus).
|

